Neural Networks in Text Mining
Overview: Neural Networks for NLP
A feed forward artificial neural network (ANN) designed to predict sentiment analysis in climate change discourse
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Neural_Network_Apr_2020-01-5f4088dfda4c49d99a4d927c9a3a5ba0.jpg)
Here is a link to the Wikipedia page for more information on neural networks.
Implementation Details
Data Preparation
The text data preparation involved a comprehensive multi-stage process to ensure high-quality inputs for the neural network model:
-
Data Collection and Loading
- Loaded data from multiple JSON files containing Reddit comments and news articles
- Used custom functions (
load_reddit_commentsandload_news_articles) to parse these files - Created a combined corpus by concatenating data from both sources with source labels
- Initial dataset had 8,448 documents with a text field and source field (Reddit vs news)
-
Automatic Labeling
- Implemented a lexicon-based approach using keyword matching
- Created two sets of keywords:
- Positive keywords: climate, global warming, renewable, carbon neutral, sustainability, etc.
- Negative keywords: climate hoax, fake science, scam, not real, climate agenda, etc.
- Created a robust labeling function (
very_robust_auto_label) that:
- Counted occurrences of positive and negative keywords in each text
- Assigned label 1 (positive) if more positive keywords than negative
- Assigned label 0 (negative) if more negative keywords than positive
- Assigned label -1 (neutral/unclear) if equal or no matches
- Initially labeled data was highly imbalanced:
- 7,624 neutral/unclear (-1)
- 763 positive (1)
- 61 negative (0)
-
Dataset Filtering and Balancing
- Filtered out neutral/unclear documents (label -1)
- Resulting in 824 labeled documents (763 positive, 61 negative)
- Used scikit-learn's
resampleto balance the dataset:
- Identified majority class (positive) and minority class (negative)
- Upsampled the minority class with replacement to match majority class size
- Combined original majority samples with upsampled minority samples
- Final balanced dataset contained 763 samples of each class (1,526 total)
- Note on upsampling with replacement: Each of the 61 negative samples appears approximately 12-13 times in the final balanced dataset
-
Feature Engineering
- Used CountVectorizer for text representation:
- Removed English stop words
- Set maximum features to 10,000
- Converted to lowercase
- Transformed text into a sparse matrix of token counts
- Resulting feature matrix had shape (824, 6392) before balancing
- After balancing and applying CountVectorizer, produced properly balanced input features
-
Train-Test Split
- Split the balanced dataset into training and testing sets (80%/20%)
- Used stratified sampling to maintain class balance in both sets
Neural Network Architectures
Feed-Forward Deep Neural Network
A multi-layer feed-forward neural network designed for sentiment analysis of climate-related text. This architecture processes text data after vectorization to classify sentiment as positive or negative.
Key Components:
- An input layer with 6392 features (from your CountVectorizer)
- A dense hidden layer with 128 neurons followed by dropout
- A second dense hidden layer with 64 neurons followed by dropout
- An output layer with a single neuron (for binary classification)
Model Summary:
| Layer (type) | Output Shape | Param # |
|---|---|---|
| dense (Dense) | (None, 128) | 818,304 |
| dropout (Dropout) | (None, 128) | 0 |
| dense_1 (Dense) | (None, 64) | 8,256 |
| dropout_1 (Dropout) | (None, 64) | 0 |
| dense_2 (Dense) | (None, 1) | 65 |
Total params: 826,625 (3.15 MB)
Trainable params: 826,625 (3.15 MB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 B)
# Model architecture implementation
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Dropout
def create_model(input_dim=6392):
model = Sequential([
Dense(128, activation='relu', input_dim=input_dim),
Dropout(0.2),
Dense(64, activation='relu'),
Dropout(0.2),
Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
return model
Model Development
This is a classic deep learning approach for text classification, with the following key characteristics:
- Text is first transformed into numerical features using the Bag-of-Words approach (CountVectorizer)
- The neural network then learns patterns in these feature vectors
- The output is a binary prediction (positive/negative sentiment)
- The model is used to classify text related to climate/environmental topics, with balanced classes for equal representation of positive and negative sentiment examples
Training Process
# Training process for the model
def train_model(model, X_train, y_train, X_val, y_val):
history = model.fit(
X_train, y_train,
epochs=10,
batch_size=32,
validation_data=(X_val, y_val),
callbacks=[
tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_loss',
patience=3,
restore_best_weights=True
)
]
)
return history, model
Training Results:
Epoch 1/5 39/39 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 10ms/step - accuracy: 0.6128 - loss: 0.6437 - val_accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 0.3749 Epoch 2/5 39/39 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 6ms/step - accuracy: 0.9896 - loss: 0.2916 - val_accuracy: 0.9967 - val_loss: 0.0542 Epoch 3/5 39/39 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 7ms/step - accuracy: 1.0000 - loss: 0.0373 - val_accuracy: 0.9967 - val_loss: 0.0167 Epoch 4/5 39/39 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 9ms/step - accuracy: 1.0000 - loss: 0.0090 - val_accuracy: 0.9967 - val_loss: 0.0118 Epoch 5/5 39/39 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 7ms/step - accuracy: 1.0000 - loss: 0.0044 - val_accuracy: 0.9967 - val_loss: 0.0119
Model Performance & Evaluation
The neural network achieved excellent performance on the sentiment classification task:
- Training accuracy: 100% by the third epoch
- Validation accuracy: 99.67%
- Training loss: Reduced from 0.6437 to 0.0044
- Validation loss: Stabilized around 0.01
The model shows strong convergence with minimal signs of overfitting, as indicated by the close alignment between training and validation metrics after epoch 2.
Confusion Matrix
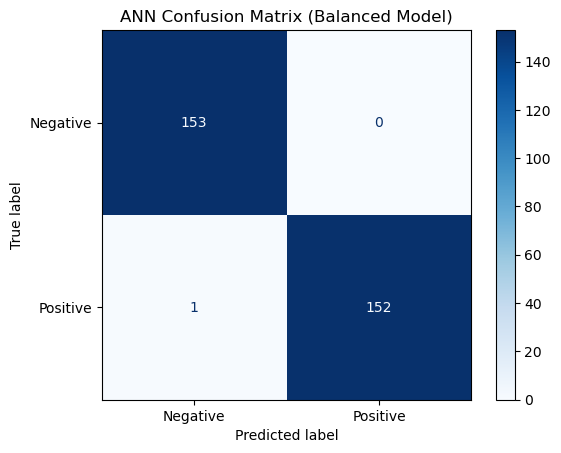
Classification Report
precision recall f1-score support
Negative 0.99 1.00 1.00 153
Positive 1.00 0.99 1.00 153
accuracy 1.00 306
macro avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 306
weighted avg 1.00 1.00 1.00 306
Insights & Conclusions
The neural network sentiment analysis model revealed several interesting patterns in climate change discourse:
Key Word Analysis
By examining the most frequent words in each sentiment class, we gained valuable insights into the language patterns associated with positive and negative sentiment in climate discourse:
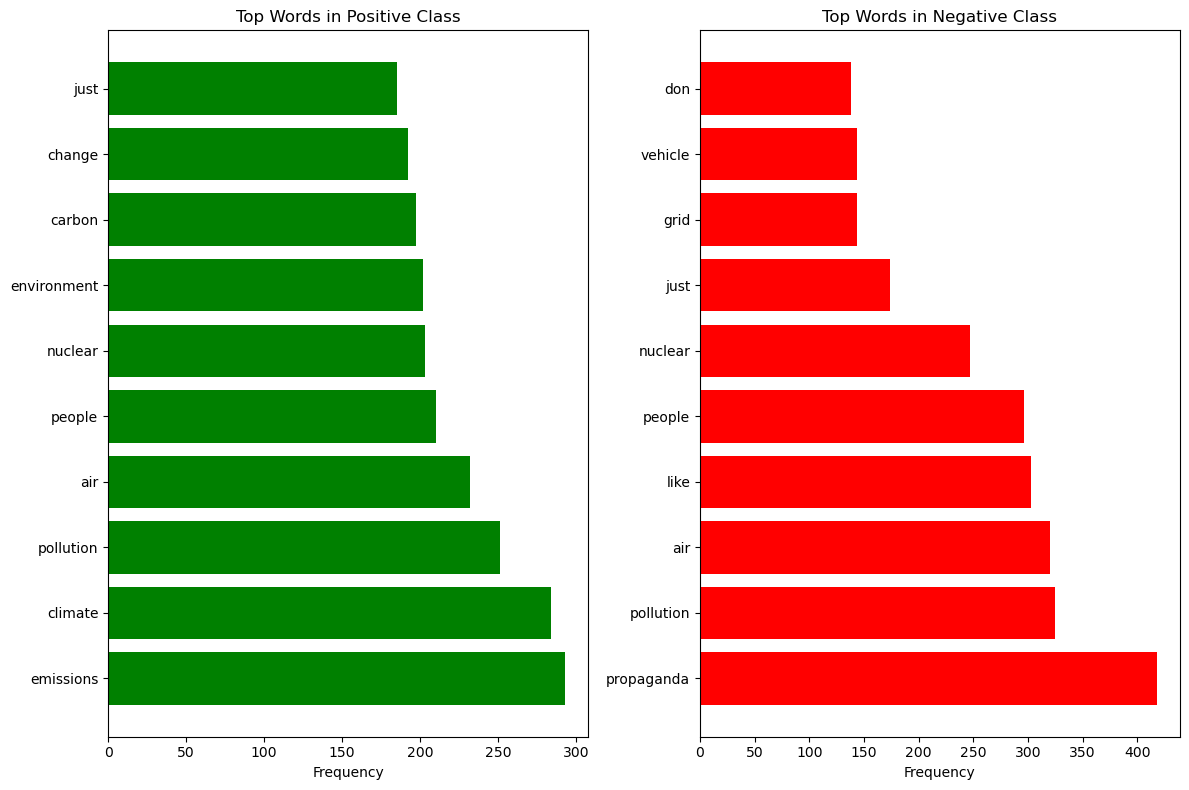

Main Findings
- Terminology Differences: Positive sentiment texts frequently use scientific and action-oriented terms like "emissions," "climate," and "pollution," focusing on the environmental impact.
- Skepticism Markers: The term "propaganda" appears as the most frequent word in negative sentiment texts, suggesting skepticism about climate change information.
- Shared Vocabulary: Interestingly, both positive and negative classes share terms like "nuclear," "people," and "air," but likely use these in different contexts.
- Technical vs. Political Framing: Positive texts appear to use more technical environmental language, while negative texts contain more politically charged terminology.
Implications
These findings suggest that sentiment around climate change follows distinctive linguistic patterns that machine learning models can effectively detect. The neural network's high accuracy (99.67%) demonstrates that these patterns are consistent enough to enable reliable automated sentiment classification.
The difference between my results with Support Vector Machines (SVM) and this feed-forward neural network is that the neural network is able to capture more complex patterns in the data, as well as my performace in preparing the data for supervised machine learning.
For broader reflections on what I've learned through this text mining journey, check out my project conclusions.